
November 5, 2019
If you’re new to plant-based eating, knowing easy swaps and substitutions can save you time, stress, and money. Here’s a simple guide to replacing animal ingredients with plant-based ingredients. As you’ll see, it’s pretty straightforward.
Broadly speaking, milk is perhaps the easiest animal food to substitute. Not only can you find plant milks that taste delicious, they are widely available in grocery stores. And when it comes to cooking or baking, if a recipe calls for dairy milk, you can almost always just use the same measurement of a plant-based milk. Soy, almond and coconut are the most commonly found plant milks, but there are now many more to choose from including rice, cashew, macadamia, oat, flax, pea and hemp. There are even plant-based creamers for your coffee. Be sure to take a look in both the refrigerator section and cartoned milk section at the grocery store to see what’s available. Try a few options until you find the one you prefer.
Eggs in recipes:
 Eggs in recipes can be replaced in a variety of ways but the “golden standard” is a quick and inexpensive flax/water blend. The ratio is: 1 tablespoon of flaxseed meal (ground raw flaxseed) to 3 tablespoons of water. You simply combine the flax and water in a bowl, stir, and let it sit for five minutes to thicken. This replaces the equivalent of one egg in a recipe. So if a recipe calls for two eggs, double it, etc. Alternate egg replacement recipes include: mashed banana, unsweetened applesauce, chia seeds, silken tofu, baking soda and vinegar and even canned pumpkin. There are also several brands of plant-based egg replacer (these can be found in the baking aisle of the grocery store or online). While this substitution works for many recipes, for optimal results, we recommend finding a plant-based recipe to work from rather than “plantifying” a standard recipe. Check out our recipes for egg-free french toast, spelt blueberry pancakes, and coconut waffles.
Eggs in recipes can be replaced in a variety of ways but the “golden standard” is a quick and inexpensive flax/water blend. The ratio is: 1 tablespoon of flaxseed meal (ground raw flaxseed) to 3 tablespoons of water. You simply combine the flax and water in a bowl, stir, and let it sit for five minutes to thicken. This replaces the equivalent of one egg in a recipe. So if a recipe calls for two eggs, double it, etc. Alternate egg replacement recipes include: mashed banana, unsweetened applesauce, chia seeds, silken tofu, baking soda and vinegar and even canned pumpkin. There are also several brands of plant-based egg replacer (these can be found in the baking aisle of the grocery store or online). While this substitution works for many recipes, for optimal results, we recommend finding a plant-based recipe to work from rather than “plantifying” a standard recipe. Check out our recipes for egg-free french toast, spelt blueberry pancakes, and coconut waffles.
Eggs for breakfast:
If you want to replace eggs in their own right, check out our tofu scramble, huevos rancheros, or experiment with one of the new plant-based egg alternatives on the market (you can now find these at most good grocery stores, usually in the refrigerator/egg section).
Butter in recipes and for cooking can easily be swapped with plant-based butters, margarines, oils and sprays. Healthier alternatives include avocado or nut butters, depending on the recipe.
Cheese can be swapped for one of the many different types of plant-based cheeses, including cheddar, mozzarella, feta and brie. Plant-based cheeses are available in many grocery stores, and range from more refined to less. Several brands make excellent plant-based parmesan, but for a simple and cost effective option try substituting nutritional yeast, which has a distinctive cheese-like flavor that can also be used to add depth and flavor to pasta dishes or sprinkled on top of popcorn. Additionally, plant-based cheeses are simple to make at home from nuts or seeds. Almond cheese, for example, is a great substitute for ricotta, and cashew cheese can be used in place of brie. There are plenty of basic (and not so basic!) recipes available online.
As with milks and cheeses, there are a wide range of plant-based yogurts available in stores including almond, soy and coconut varieties. As always, choose the option that best suits your taste, performance, and health goals.
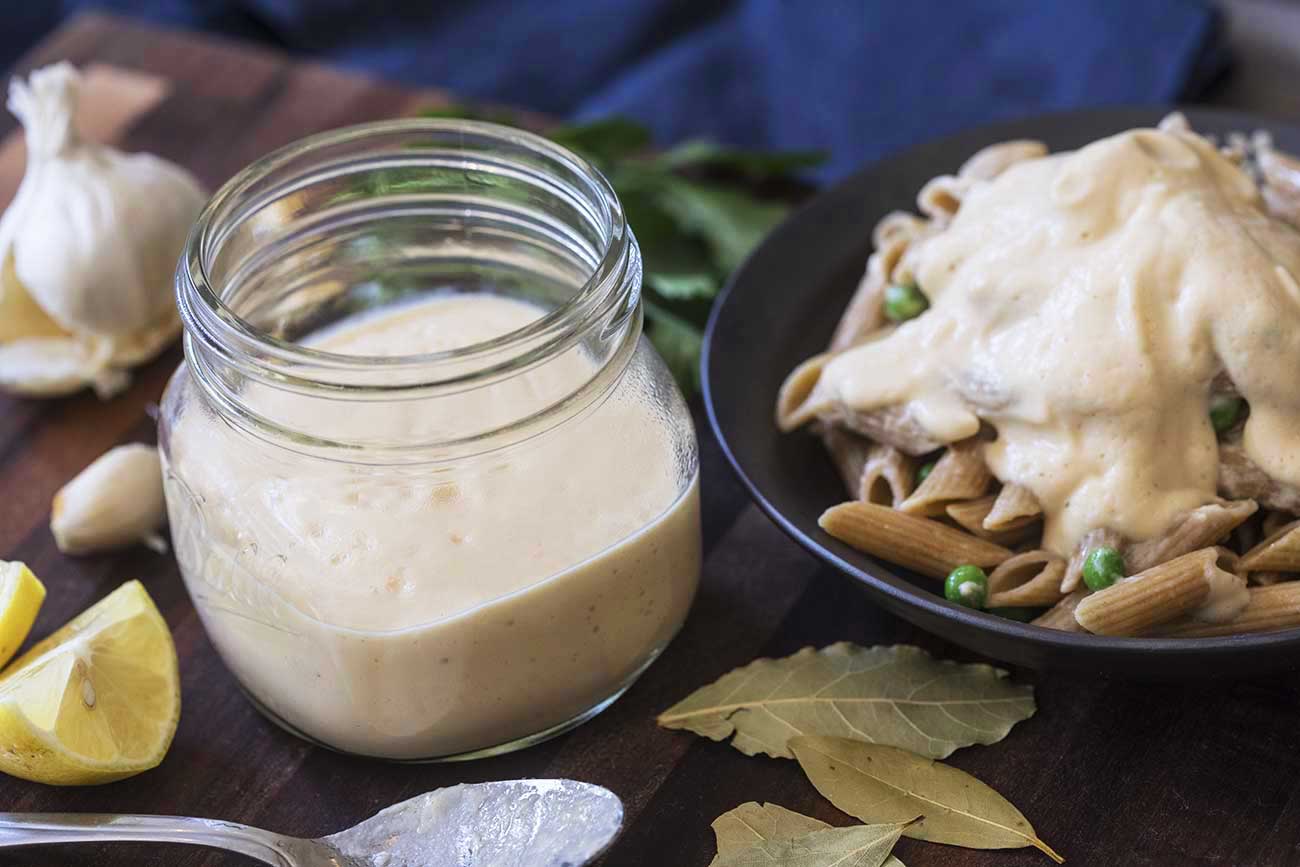
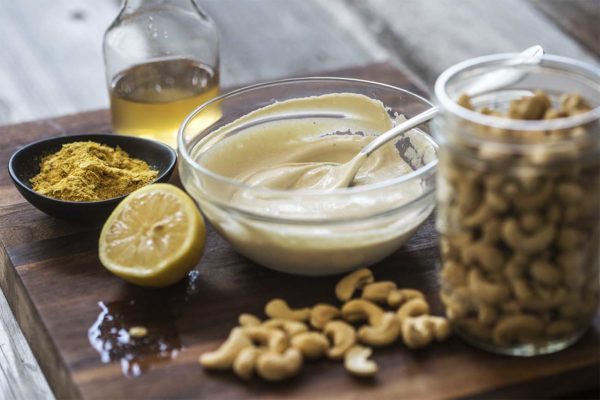 Sauces, Dressings, and Condiments
Sauces, Dressings, and CondimentsMany pre-made sauces, dressings and condiments are already plant-based, and there are also loads of affordable plant-based alternatives to traditionally animal-based ones available in grocery stores and online. On our Recipes page you’ll also find recipes for several of our favorite home-made versions, including: gravy, BBQ sauce, cashew sour cream, buffalo tahini sauce, bolognese sauce, Alfredo cream sauce, and sweet vanilla cream. These sauces are great because they can be made in big batches and kept in the fridge and/or freezer.
The range of meat substitutes, both store-bought and home-made, are nearly limitless. While plant-based meats can range from healthy to healthier, many recipes work well with whole foods like tofu, tempeh, lentils and beans. Additionally, since the vast majority of the population are not gluten-intolerant, seitan (a wheat protein product) is also a great option.
While store-bought fish substitutes are fairly new to the market, there are many home-made recipes that imitate the taste and texture of various types of fish. Various types of seaweed, including nori, kombu, and wakame, can also be used to make dishes taste ‘fishy’.
Many athletes and other active people use protein powder to bolster their daily protein intake. Whey, egg, beef and other animal-based protein powders can be easily swapped for one of the many plant-based protein powders available in stores and online, including pea, soy, brown rice, hemp, and blended proteins.
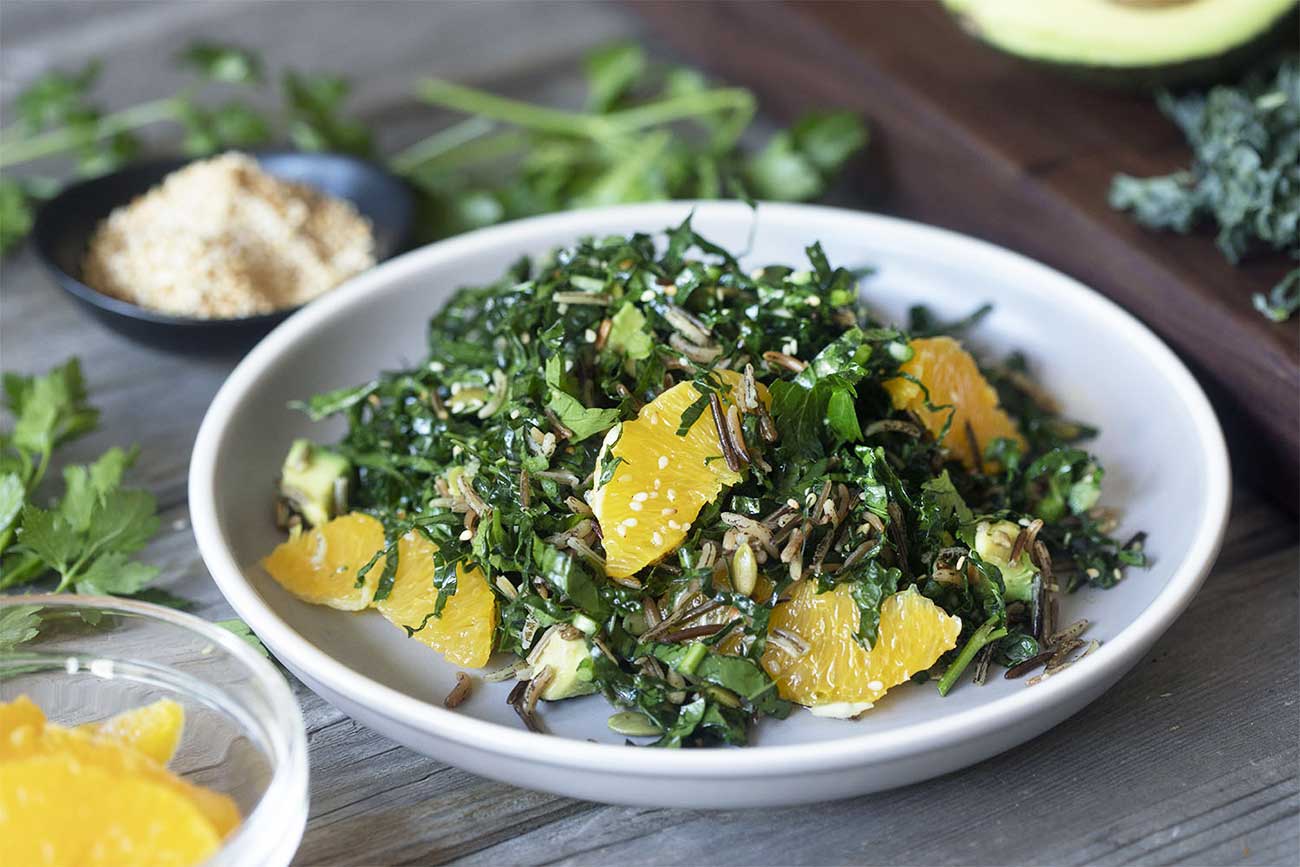

Important Nutrients
It’s easy to get all the nutrients we need to thrive eating a plant-based diet. Plant-based diets are typically higher in quality than diets that include meat (1) and include […]
More Details
How Much Protein Do You Need?
Protein is one of the main building blocks of the body, helping us grow and repair tissue, while also helping our hormone and immune systems function properly. Important as it […]
More Details
6 Ways To Get Started on a Plant-Based Diet
When it comes to making food choices, everyone has their own goals and their own rate of change. Some people cut out animal products entirely, while others start by including […]
More Details